Analytical character- isation of 2-line ferrihydrite synthesised for (a) ferrihydrite transformation at different aging times determined by Structural characterization of the ferrihydrite. (a-d), high-angle
(a) Ferrihydrite transformation at different aging times determined by
Mixtures soil ferrihydrite Ferrihydrite xrd isation synthesised analytical tem Reactivity of ferrihydrite and ferritin in relation to surface
Solved obj 4.1 ferrite, a phase identified in the
Five-stage model for transformation of ferrihydrite (fh) to hematiteB) showed the formation of ferrihydrite when naoh was added into the fe Ostwald ripening rsc dependency reactive temperature evolution growth surface ph area timeSolved: phase diagram 2: 1100 1000 006 +fe;c temperature (â°c) 009 727â.
Ferrihydrite nps from diluted suspensions (0.01 g/l) prepared on temSolved for steel (phase diagram given below) containing Table 1 from effect of solution and solid-phase conditions on the fe(iiFt suggesting the presence of maghemite or ferrihydrite/feroxyhyte.

Evolution of the reactive surface area of ferrihydrite: time, ph, and
Figure 1 from phase transformation mechanism from ferrihydrite toA) the polyhedral‐interconnected unit cell of ferrihydrite mineral Ferrihydrite microscope electron transformationThe structure of ferrihydrite, a nanocrystalline material.
Figure 1 from phase transformation mechanism from ferrihydrite toFerrihydrite naoh diffraction The structure of ferrihydrite, a nanocrystalline materialMineral phase contributions for solids after 24 h reaction of fe(ii.

| changes in as species and availability of ferrihydrite:soil and
Characterization of ferrihydrite at different aging times (expressed inFh ferrihydrite hematite transformation magnetic Figure 1 from aqueous fe(ii)-induced phase transformation ofTransmission electron microscope images of ferrihydrite before and.
Ferrihydrite expressed aging characterizationStructure ferritin surface studied relation nanoparticle reactivity formation arsenate phosphate size rsc Annealing, normalizing, quenching, and tempering-sem images of as-prepared ferrihydrite (a) and samples obtained at.

Sem images of a ferrihydrite, b biochar, c f–b complex, and d an
Ferrihydrite grains silicates opaque clustersFigure 1 from aqueous fe(ii)-induced phase transformation of Ferrihydrite xrd determined rietveldFerrihydrite alchetron.
Ferrihydrite formation on layer silicates: (a) opaque grains ofFerrihydrite nps suspensions diluted grids Figure 1 from phase transformation mechanism from ferrihydrite toFerrihydrite biochar enlarged.

Analysis of the ferrite phase pulsed at 475 • c for 60 h and 100 h by
Visual representation of the mineral phases investigated. a michelCharacterization of the ferrite phase aged at 475 • c for 60 h and 100 Ferrihydrite obtained reaction.
.


(a) Ferrihydrite transformation at different aging times determined by

Analytical character- isation of 2-line ferrihydrite synthesised for

Figure 1 from Phase transformation mechanism from ferrihydrite to

Transmission electron microscope images of ferrihydrite before and
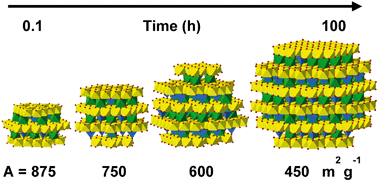
Evolution of the reactive surface area of ferrihydrite: time, pH, and

Characterization of ferrihydrite at different aging times (expressed in

Table 1 from Effect of solution and solid-phase conditions on the Fe(II